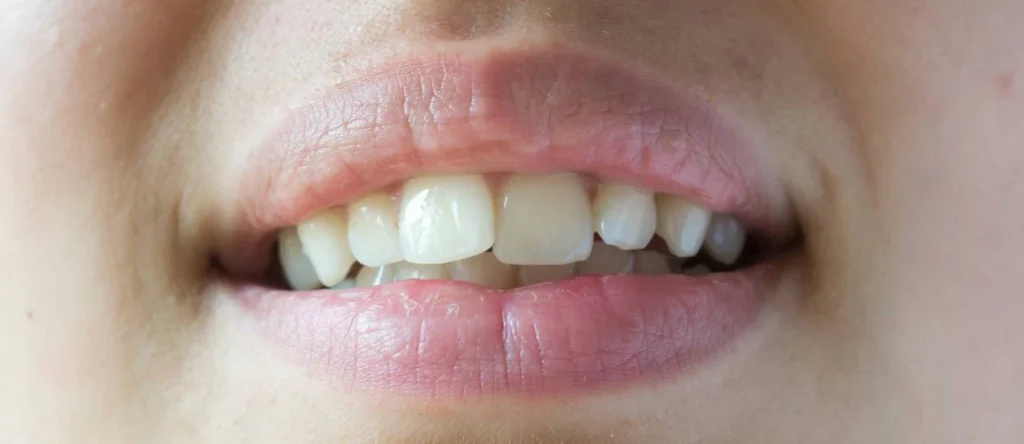
A crossbite is a common orthodontic issue in which one or more upper teeth bite inside the lower teeth rather than aligning correctly. While sometimes subtle, crossbites can lead to uneven wear of teeth, gum problems, jaw pain, and even asymmetrical facial growth if left untreated. Early detection and intervention are essential to prevent long-term complications and improve both function and aesthetics. This article explores the causes, principles, treatments, and lifestyle considerations for managing crossbites effectively through modern orthodontic care.
What Is a Crossbite?
A crossbite occurs when the upper teeth sit inside the lower teeth when biting down, which can involve a single tooth (posterior crossbite) or multiple teeth (anterior crossbite). Causes may include genetics, delayed or abnormal jaw development, overcrowding, or prolonged habits like thumb sucking. Symptoms may range from misaligned bite and difficulty chewing to jaw discomfort and uneven enamel wear. If untreated, crossbites can contribute to gum recession, tooth fractures, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems. Early evaluation allows orthodontists to determine the best course of treatment to restore proper bite alignment.
Principles of Orthodontic Correction for Crossbite
Correcting a crossbite relies on controlled movement of teeth and, in some cases, modification of jaw growth. Orthodontic appliances apply gentle, consistent pressure to reposition teeth into proper alignment while supporting healthy jaw development. Digital imaging, X-rays, and bite analysis allow precise planning of tooth and jaw movements. In growing children, early intervention can guide jaw development to prevent severe skeletal discrepancies. The overarching goal is to achieve balanced bite function, protect teeth from excessive wear, and enhance overall oral health.
Common Treatments for Crossbite
Several orthodontic treatments are used to correct crossbites. Braces apply controlled pressure to reposition teeth gradually and are effective for both mild and complex cases. Clear aligners offer a discreet option for mild to moderate crossbites and allow gradual, removable tooth movement. Palatal expanders are often used in children to widen the upper jaw, creating space for proper alignment. In severe cases, orthognathic surgery may be recommended for adults with significant jaw misalignment. Retainers are essential after treatment to maintain bite correction and prevent relapse. Each treatment is customized to the patient’s age, dental development, and severity of the crossbite.
Integrating Orthodontic Care with General Dentistry
Successful crossbite correction requires collaboration with general dentistry. Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings prevent cavities, gum disease, and plaque buildup that could complicate orthodontic treatment. Proper oral hygiene, including brushing with soft-bristled toothbrushes and flossing, is essential for maintaining tooth and gum health during treatment. Fluoride treatments and adjunctive tools such as interdental brushes or water flossers can further protect enamel and gums. Working closely with a dentist ensures the overall health of the teeth while orthodontic appliances gradually correct the bite.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Crossbite During Treatment
Lifestyle habits can significantly influence the success of crossbite treatment. Avoiding hard, sticky, or sugary foods prevents damage to braces or aligners and reduces the risk of tooth decay. Consistent attendance at orthodontic appointments ensures timely adjustments and progress tracking. Maintaining a balanced diet supports tooth and gum health, while stress management reduces habits like teeth grinding that can complicate treatment. Using protective gear during sports or physical activities prevents injury to orthodontic appliances. These measures, combined with professional care, promote effective crossbite correction and long-term oral wellness.
FAQ’s
At what age should a crossbite be treated?
Early evaluation around age seven is recommended, but treatment can be effective in adolescents and adults depending on severity.
Can clear aligners correct a crossbite?
Clear aligners are effective for mild to moderate crossbites, but severe cases may require braces or palatal expanders.
Is crossbite treatment painful?
Mild discomfort or pressure is common during adjustments, but it typically subsides within a few days.
How long does crossbite treatment take?
Duration depends on severity and treatment type, ranging from several months for minor cases to 2–3 years for complex corrections.
Will the crossbite return after treatment?
Retainers are essential to maintain results and prevent relapse, ensuring long-term bite stability.
Conclusion
Correcting a crossbite is essential for preventing dental complications, improving bite function, and enhancing smile aesthetics. Orthodontic treatment aligns teeth, supports jaw development, and protects oral structures from long-term wear and damage.
When combined with proper oral hygiene, routine dental care, and healthy lifestyle practices, orthodontic intervention provides a comprehensive solution for crossbites. Early and consistent care ensures functional, balanced, and attractive smiles that contribute to lifelong oral health and overall well-being.